Chronic Pain and Work Rehabilitation
Bio-psychosocial Model
Chronic Pain Vicious Cycle
Biological: pain, muscle spasm, joint stiffness, muscle weakness, decrease social activities
Psycho-social: Anxiety, Stress, Depression, Fear Avoidance, Poor sleep

Multidisciplinary Team Approach
Ergonomic Advice:
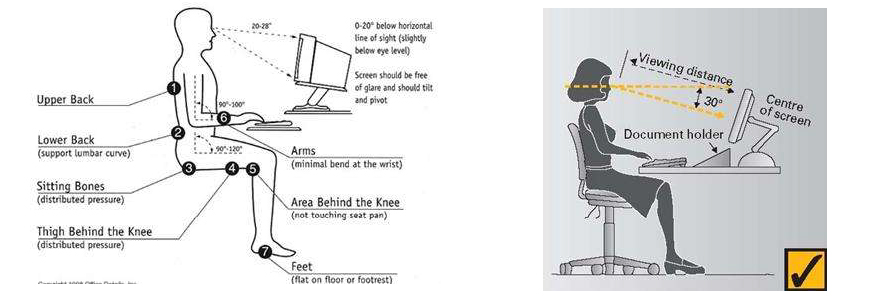
Sitting
Typing

Position of the screen
Breaks
References:
A handbook for workplaces: Officewise-A guide to health and safety in the office
Office environment & worker safety & health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Chronic Pain Vicious Cycle
Biological: pain, muscle spasm, joint stiffness, muscle weakness, decrease social activities
Psycho-social: Anxiety, Stress, Depression, Fear Avoidance, Poor sleep

Multidisciplinary Team Approach
- Physiotherapy
- Rehab doctor
- Rheumatology specialist
- Anesthesiologist with special training in Pain
- Clinical Psychologist
Ergonomic Advice:
Sitting

- Sit with your hips as far back as they can go in the chair.
- Adjust the seat height so your feet are flat on the floor and your knees nearly equal to your hips level.
- Adjust the back of the chair to a 100°-110° reclined angle with your upper and lower back well supported by the back of the chair.
- Adjust the armrests (if fitted) so that your elbows are well supported and shoulders are relaxed.
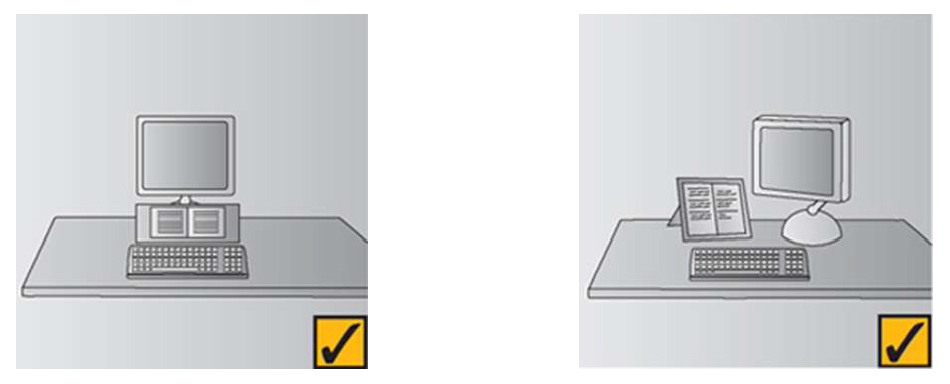
Typing

- Make sure the keyboard is close enough to you.
- Place the keyboard directly in front of your body.
- Adjust the keyboard height so that your shoulders are relaxed, your elbows are in a slightly open position (90° to 100°), and your wrists and hands are straight.
- An articulating keyboard tray can be a good option for placing the input devices at the arm rest level. But it should not push you too far away from reaching other material from the desk.
- The tilt of your keyboard is dependent upon the reclined angle of the seat. If you are sitting reclined, a slight increase in the tilting of the keyboard is better. It make sure your wrist is in a neutral position when typing. Wristrest is a good device to maintain neutral posture of the wrist.
- Place the mouse, mouths pad or pointer as close as possible to the keyboard.
Position of the screen

- Place the screen directly in front of you, above your keyboard.
- Position the top of the screen approximately 2-3” above seated eye level.
- Sit at least an arm's length away from the screen.
- Reduce glare by careful positioning and adjusting the vertical screen angle of the screen.
- Either placing the source documents directly in front of you, between the screen and the keyboard or fix it on a document holder positioned adjacent to the screen.
- Place your telephone within easy reach.
- Use headsets and speaker phone to eliminate cradling the handset.
Breaks
- Take short 1-2 minute stretch breaks every 20-30 minutes. Take a 5-10 min break after each hour of work.
- Resting and refocusing your eyes periodically to avoid fatigue. You can also look away from the monitor and focus on something in the distance periodically..
References:
A handbook for workplaces: Officewise-A guide to health and safety in the office
Office environment & worker safety & health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention

